EU-MORE at Coiltech Germany in Mar 2024
Trends in motor technologies, and why old electric motors should be replaced faster – presented by the EU-MORE project at Coiltech trade show & World Magnetic Conference in Augsburg end of March 2024.
Early 2024, EU-MORE has reached its next milestone with the publication of a comparative review on motor technologies, including an analysis of motor system optimization benefits. MEPSs for motors have led to major improvements in the energy efficiency of motors, which now reach levels known as Super- and Ultra-Premium Efficiency Motors (IE4 and IE5). This review discusses the latest trends in IM, SynRM and PM, highlights some aspects of direct-on-line starting motors. The review also digs into the energy saving potential of VSDs, further digitalization and other types of system optimization.

EU-MORE D2.2 – Review of past and existing policies for the acceleration of electric motor renovation [LIGHT VERSION]
The Light Version of the EU-MORE Policy Review includes the report's results, the country review template adopted and a summary table of the analysed policy measures.

EU-MORE D2.2 – Review of past and existing policies for the acceleration of electric motor renovation [FULL VERSION]
Electric motors for industrial applications have the tendency to stay in service longer than their expected lifetime and be replaced only at their end-of-life, limiting the benefits of the higher efficiency of new motors. The EU-MORE project aims to capture the benefits of accelerating the replacement rate of old, inefficient motors through the development of new policies. To accomplish this, a review of past and existing policies targeting industrial electric motors has been conducted for 27 European Member States. The review encompasses 64 policy measures targeting directly and indirectly the early replacement of motors as a measure to improve energy efficiency in industries. Each policy measure is presented with a short description, responsible authority, status, issue date, start date, end date, duration, and reference to the official publication. Additionally, a preliminary estimation of the impact of the analysed measures has been conducted.
The review methodology is based on the contribution of several country experts able to provide a high-level perspective on the national policies under exam.
The results show a strong predominance of financial measures, mostly subsidies and loans (or combinations of them), followed by mandatory standards, fiscal measures and voluntary agreements. The review highlighted a very low implementation of measures targeting trainings and information, particularly relevant for industrial SMEs. On a national level, Germany resulted the country with the highest number of measures involving electric motors, followed by Austria. Very few national policies include systemic approaches to motor systems (i.e. including the overall supply of motive power as well as the demand side for motive power), which generate usually the highest energy savings, as evidenced from case studies.
The report is complemented by an in-depth presentation of measures directly targeting industrial electric motors across the Member States.
The Full Version of this deliverable includes the review reports of the 27 Member States.

Speeding up the adoption of state-of-the-art electric motors
The European project EU-MORE (an acronym for EUropean MOtor REnovation initiative) aims at seizing the benefits deriving from the acceleration of the replacement rate of old inefficient motors through the development of new policies.

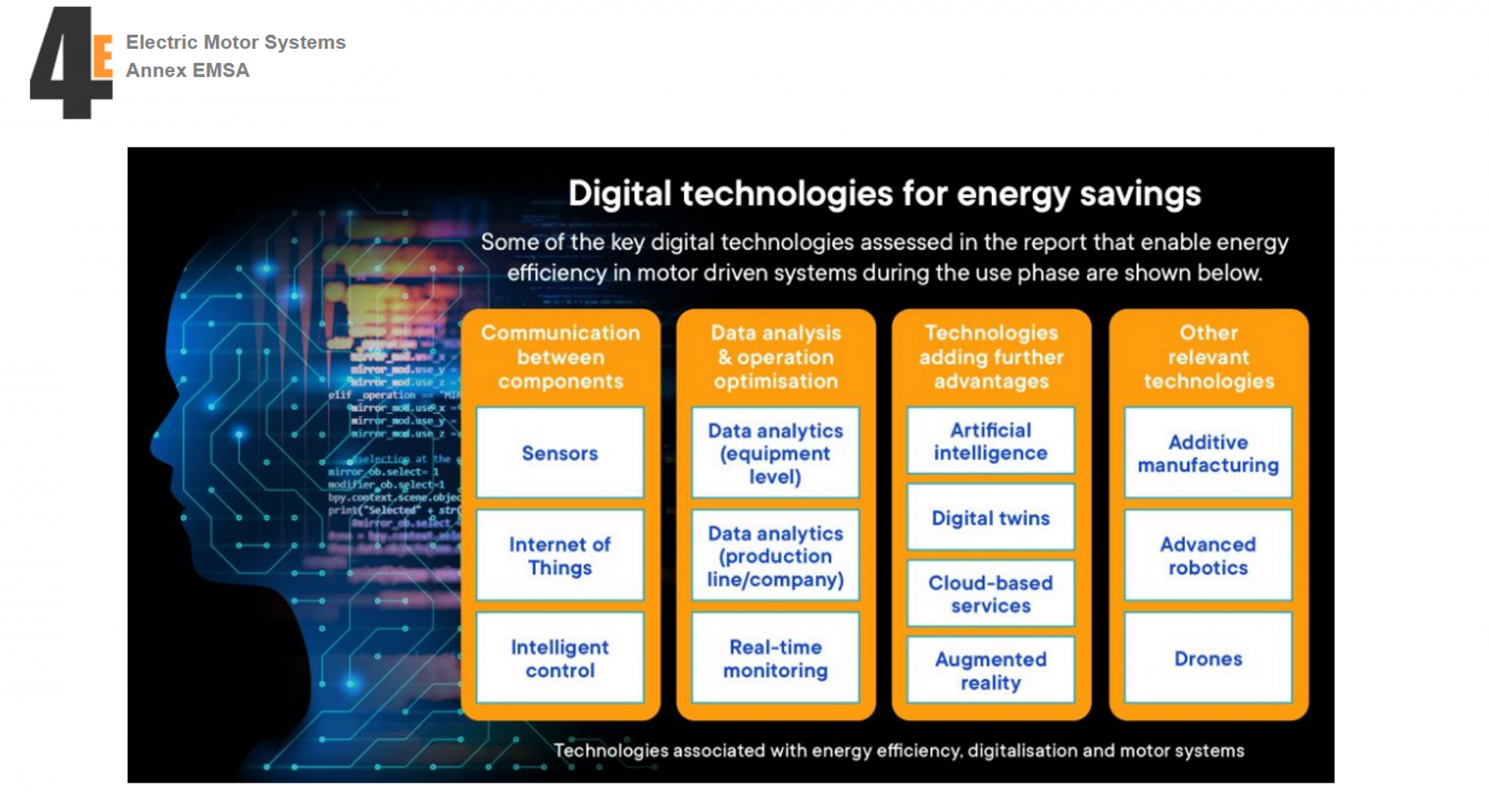
EMSA policy brief: Key findings on digitalisation technologies for motor systems
This Policy Brief gives an overview of the content of the EMSA report on
Classification of digitalisation technologies for electric motor driven systems.
The report identifies 13 digital technologies with the potential to influence energy
consumption in electric motor driven systems and contains definitions, descriptions and examples in this area.

Perspectives on Electric Motor Market Transformation for a Net Zero Carbon Economy
New paper by
Anibal T. de Almeida , Fernando J. T. E. Ferreira and João Fong
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, ISR-University of Coimbra, Portugal
As electric motors systems represent such a large share of the overall electricity consumption (over 50%), large savings potential could be made available by the use of energy-efficient motor systems both in new installations and by accelerating the replacement of old inefficient motors. Since electric motors are very reliable, their lifetime is long (according to recent studies it may exceed 20 years) which translates into a very inefficient existing stock despite worldwide policy efforts. This paper analyzes the current efficiency of the installed stock and the causes for its low efficiency, possible policy options to increase its the efficiency, the role of new technologies and improvements possible by targeting the entire motor system at the time of motor replacement. The paper presents an innovative analysis of the estimated impact of increasing the uptake of high-efficiency motors and motor systems; effective policies could translate into 100 TWh/year in the European Union if additional measures, such as addressing oversizing, proper controls (VSDs) and digitisation, are also implemented

ENERGY-EFFICIENT ELECTRIC MOTORS AND MOTOR SYSTEM
Improving energy efficiency is the fastest, cheapest and cleanest way to get reliable power to more people. Well over half of the world's electricity is consumed
by just four products: electric motor systems, lighting, room air conditioners, and residential refrigerators.

ENERGY EFFICIENT INDUSTRIAL MOTORS
Electric motors are of utmost importance in industrial as well as agriculture sector. These motors found their application as constant speed drives with very low rating as well as variable speed drives with very high rating. This paper describes the various factors affecting the efficiency of motor and method to increase it on the basis of comparison with various standards. An incremental difference in the efficiency is also discussed.

